In this decision, the appellant criticises the COMVIK approach on several points. The Board disagrees. With regard to inventive step, according to the Board, there is a lack of “technical purpose” according to T1227/05.
Information from the author: “technical purpose” is no longer sufficient according to decision G1/19 for non-technical features to make a technical contribution. According to current case law (as of August 2024), in such a case a further or intended or implied technical use is required.
Object of the Invention:
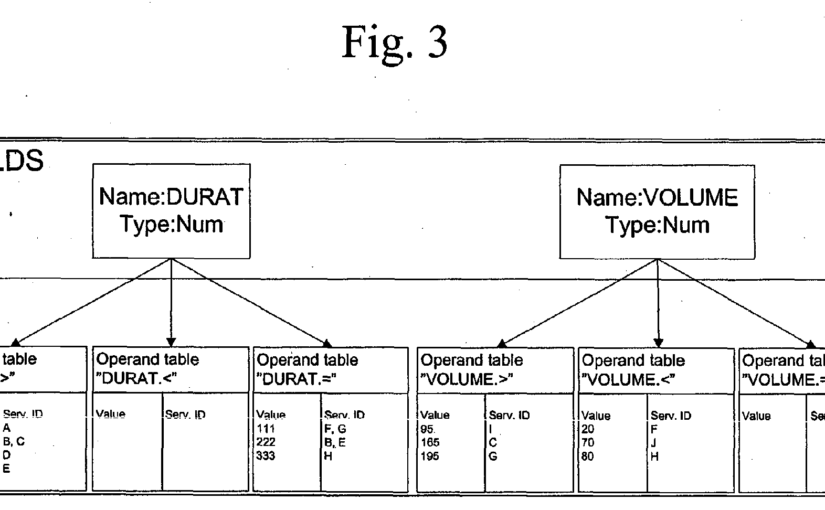
- data records, e. g. the duration and data volume of a telecommunication connection, that are sorted into service classes, in particular for rating and billing purposes
- identifying the class of a service from a data record forms a performance bottleneck once the number of services is increased to the thousands
- the application seeks to provide a method which can handle large numbers of service classes more efficiently than the conventional use of conditional statements does
- the solution is based on reducing, as a first step, a large number of service classes into specific sets
- these sets are then intersected in a final step
- this algorithm classifies data records more efficiently
Board (COMVIK approach):
- it would appear paradoxical to the Board to recognise an inventive step on the basis of a non-technical innovation (such as an organisational, administrative, commercial or mathematical algorithm) having no technical implication other than the (obvious) desire for its implementation on a general-purpose computer
Appellant I (COMVIK approach):
- claimed subject-matter as a whole should be examined for the presence of an inventive step once the subject-matter as a whole has been found to meet the technology criterion of Article 52(1)(2)(3) EPC
- Article 56 EPC 1973 should be applied independently of Article 52(1)(2)(3) EPC because Article 52(2) EPC has to be applied independently of Article 56 EPC 1973
Board I (COMVIK approach):
- the Board does not accept such formal reasoning and points out that it is normal and often necessary for legal provisions to be in an asymmetric relationship or hierarchical dependency
- for example, the novelty of a claim has to be examined independently of inventive step considerations, whereas a finding of inventiveness presupposes a novelty examination
- another example is the validity of a priority claim which has to be checked independently of novelty and inventive step requirements, whereas novelty and inventive step cannot be established independently of the validity of a priority right.
Appellant II (COMVIK approach):
- regarding the Board’s insistence on a technical problem when applying the problem-and-solution approach, the appellant disputes that such a requirement can be deduced from the EPC or introduced from its Implementing Regulations
- the appellant refers inter alia to decision T 473/08 (by a different Board) to point out that “a non-technical problem can have a technical solution“
Board II (COMVIK approach):
- there is no divergence, the Board agrees to the statement that a non-technical problem can have a technical solution
- on the other hand, where an intrinsically non-technical solution (mathematical algorithm) seeks to derive a technical character from the problem solved, the problem must be technical
- this is the point on which the present case hinges
Appellant III (COMVIK approach):
- another argument of the appellant refers to the legislative history of the EPC (travaux préparatoires) which is said not to provide any explicit support for a cumulative application of Article 52(2) EPC and Article 56 EPC 1973
Board III (COMVIK approach):
- the restriction of substantive patent law to technical subject-matter is so self-evident that the founding fathers of the EPC did not even mention that requirement in the original (1973) version of Article 52(1)
- the explicit clause “in all fields of technology” was not added to Article 52(1) until the Diplomatic Conference in the year 2000 harmonised the Article with the TRIPs treaty
- nevertheless, Article 52(1) EPC has always been understood as referring to technical inventions
Board IV (inventive step):
- as the algorithm is a mathematical (inter alia Boolean) method and mathematical methods as such are deemed to be non-inventions (Article 52(2)(3) EPC), a technical character of the algorithm could be recognised only if it served a technical purpose (T1227/05)
- however, the automatic classification of data records according to claim 1 serves only the purpose of classifying the data records, without implying any technical use of the classification
- the claim covers any non-technical (e.g. administrative or commercial) use of the classified data records
- in the light of the description, the classification method prepares rating and billing procedures
- the Board does not consider the result of the algorithm — a set of classified data records — as technical
Board V (inventive step):
- enhanced speed of an algorithm, as compared to other algorithms, is not sufficient to establish a technical character of the algorithm (T 1227/05)
- if a computer-implemented algorithm runs more quickly, the resulting saving in energy is a technical effect inherent to the normal interaction of software and hardware, i.e. it is not a “further” technical effect of the algorithmic program controlling the computer (T 1173/97)
- the claimed algorithm may allow a data record to be processed in a parallel computer architecture as the various fields of a data record can be judged separately in a first level of processing
- however, claim 1 is not limited to an implementation on a parallel hardware structure
- in fact, the application as a whole is silent on parallel data processing (Parallel processing has been mentioned by the decision under appeal and addressed by the statement setting out the grounds of appeal)
- –> no inventive step